Do you ever stop and marvel at the precision of a ticking clock? That consistent rhythm that keeps our lives in sync, second by second. Well, behind every modern timepiece lies an unsung hero – quartz. Yes, that’s right! This seemingly ordinary mineral has revolutionized clock technology as we know it. Today, we delve into the fascinating world of electronics to understand how quartz in electronics has become the beating heart of our clocks and unraveled new dimensions of accuracy and reliability. Brace yourself for a journey through time as we explore just how quartz has changed the face (and mechanism) of clocks forever!
The Discovery and Development of Quartz
Centuries ago, quartz lurked in the depths of Earth’s crust, eluding human knowledge. Its crystal structure and unique properties awaited discovery. Not until the 17th century did this remarkable mineral capture the interest of scientists and researchers.
In 1670, Danish physicist and astronomer Rasmus Bartholin observed something peculiar during experiments with light passing through transparent minerals. Placing a piece of quartz between two Nicol prisms, he noted that it rotated the plane of polarized light, giving birth to the phenomenon known as “quartz birefringence” and revealing the incredible optical properties of this mysterious stone.
As time progressed, scientists delved into studying quartz’s characteristics and unlocking its potential applications. In the early 20th century, French physicists Pierre Curie and Jacques Curie discovered the piezoelectric effect exhibited by quartz crystals. They found that applying pressure to these crystals generated electrical charges—a groundbreaking revelation.
This discovery paved the way for further development in electronics. Quartz swiftly became a key component in various devices such as radios, televisions, and later, clocks. With its precise oscillations under an electric field and ability to maintain stable vibrations over time, quartz established itself as an ideal material for accurate timekeeping.
The journey from a hidden gem within Earth’s core to a cornerstone of modern clock technology has been truly remarkable for quartz. Its discovery fueled curiosity among scientists who actively unraveled its mysteries one by one, unveiling its optical brilliance and piezoelectric wonders along the way.
How Quartz Revolutionized Clock Technology
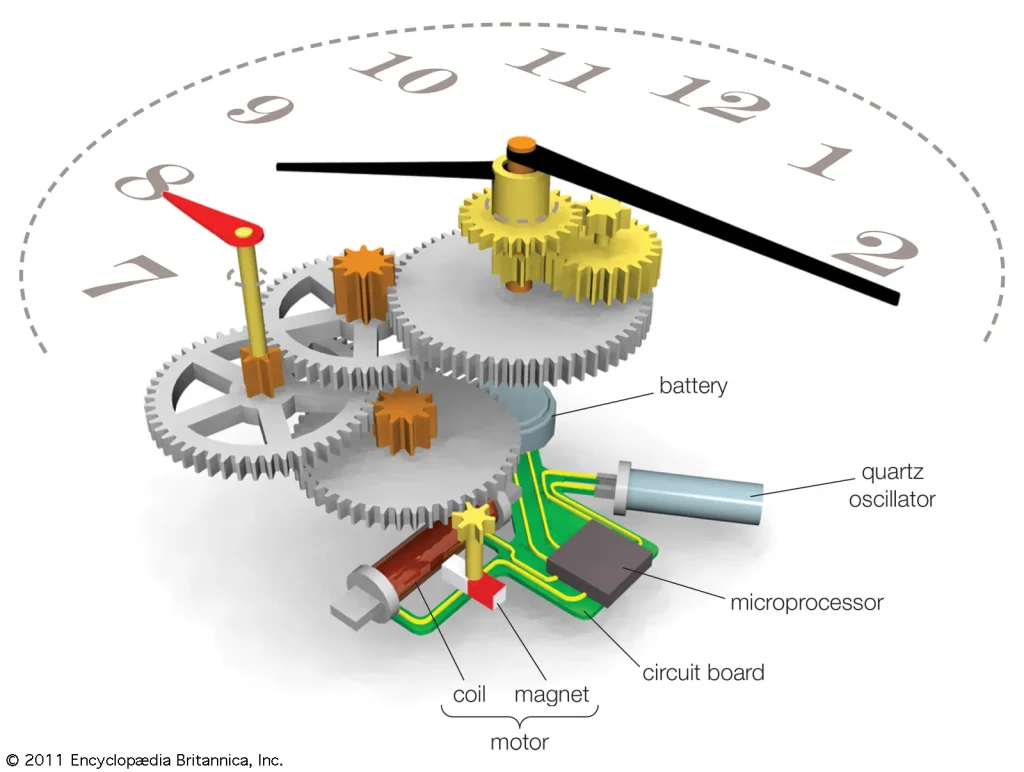
Quartz has revolutionized clock technology by providing a precise and reliable method for timekeeping. Unlike traditional mechanical clocks, which rely on gears and springs, quartz clocks utilize the piezoelectric properties of quartz crystals. Here’s a summary of how quartz has transformed clock technology:
Precise Vibrations
Quartz crystals exhibit the piezoelectric effect, vibrating at a consistent and precise frequency when an electric current is applied. This natural resonance frequency remains stable over time.
Electrical Signal Conversion
In quartz clocks, the vibrations of the quartz crystal are converted into highly accurate electrical signals through connected electronic circuits, serving as a reliable reference for timekeeping.
Accuracy
Quartz clocks offer exceptional accuracy, losing only seconds per month compared to the potential minutes or hours lost by traditional mechanical clocks.
Compact and Affordable
Quartz crystals are small and easily integrated into compact electronic circuits. Advancements in mass production techniques have made quartz clocks affordable and available in various forms, from wristwatches to wall-mounted clocks.
Low Maintenance
Fewer delicate components in quartz clocks result in lower maintenance requirements compared to traditional mechanical clocks, which often need frequent adjustments and repairs.
Versatility
The stable frequency characteristics of quartz crystals make them versatile components, widely used not only in clocks but also in various electronic devices, sensors, and communication systems.
Accessibility
The affordability and accessibility of quartz clocks have democratized accurate timekeeping, making quartz-based timepieces, including watches, commonplace in households and businesses.
Benefits of Using Quartz in Electronics for Clocks
As quartz revolutionized clock technology, here are some of the key benefits of using quartz in electronics clocks:
Exceptional Accuracy
Quartz’s natural vibrations provide a highly stable and consistent reference for timekeeping, ensuring exceptional accuracy in electronic clocks. This surpasses the precision of traditional mechanical clocks relying on springs and pendulums.
Durability and Resistance
Quartz crystals are highly durable and resistant to temperature changes and physical stress. This durability ensures that electronic clocks using quartz maintain accuracy over extended periods, requiring minimal maintenance and withstanding diverse environmental conditions.
Cost-Effectiveness
The mass production of quartz crystals contributes to cost-effective manufacturing processes. This, in turn, allows clock manufacturers to produce affordable electronic clocks on a large scale, making precise timekeeping accessible to a wide consumer base.
Miniaturization and Compact Design
Quartz’s small size and lightweight nature enable miniaturization in clock designs. Electronic clocks, including wristwatches, can easily incorporate quartz crystals into compact circuit boards. This not only enhances portability but also offers design flexibility for modern clockmakers.
Widespread Availability
The cost-effectiveness of quartz-based clocks has led to their widespread availability, making them accessible to consumers worldwide. Quartz clocks have become ubiquitous, from household wall clocks to portable devices like wristwatches.
Reliability in Various Environments
Quartz’s resistance to environmental factors ensures the reliability of electronic clocks in diverse conditions. Whether exposed to temperature variations or physical stress, quartz-based clocks maintain their accuracy, contributing to their long-lasting performance.
In summary, the benefits of utilizing quartz in electronic clocks extend to exceptional accuracy, durability, cost-effectiveness, miniaturization, and reliability. This timeless innovation has become a cornerstone in modern clock technology, shaping the way we measure time in today’s society.
Types of Quartz-based Clocks Available Today
Quartz has indeed revolutionized the world of clocks, offering a diverse range of timekeeping options to suit various preferences and needs. Let’s explore some of the popular types of quartz in electronics clocks available today:
Quartz Analog Clocks
Featuring traditional hour and minute hands, these clocks utilize the precision of quartz crystals to ensure smooth and continuous motion. They provide a classic and timeless aesthetic while benefiting from the accuracy of quartz technology.
Digital Quartz Clocks
Displaying time numerically on LED or LCD screens, digital quartz clocks are known for their accuracy and user-friendly interface. The numerical display allows for quick and easy reading of the time with just a glance.
Quartz Wall Clocks
Combining functionality with aesthetic appeal, quartz wall clocks serve as decorative timepieces suitable for various rooms in homes or offices. They come in a variety of styles and designs, adding a touch of personality to the space.
Specialized Quartz Clocks
Atomic clocks utilize advanced technology to synchronize with atomic vibrations, maintaining unparalleled accuracy. These clocks are designed for those who prioritize precise timekeeping.
Alarm Clocks
Quartz alarm clocks go beyond basic timekeeping, offering additional features such as snooze buttons and radio functions. They provide convenience and ensure that users stay punctual, whether waking up in the morning or managing appointments.
The versatility of quartz in clock technology has led to an array of innovative timekeeping devices that cater to different preferences and lifestyles. From classic analog designs to advanced digital displays and specialized features, quartz clocks continue to meet the diverse needs of consumers, providing precise and reliable timekeeping at their fingertips.
Challenges and Limitations of Quartz in Electronics
Quartz has significantly impacted clock technology in electronics, yet it faces challenges and limitations:
Temperature Sensitivity
Quartz crystals can shift frequency in extreme temperatures, affecting accuracy. Despite compensation techniques, designers must address this for reliable timekeeping in diverse conditions.
Power Consumption
While quartz clocks are energy-efficient, reliance on power sources, especially in battery-powered models, raises concerns about frequent replacements. Ongoing exploration of energy-efficient solutions and alternative power sources is essential.
Size and Design Constraints
Miniaturization of quartz crystals is challenging without sacrificing accuracy. Embedding quartz in intricate designs poses technical difficulties, limiting design flexibility. Innovations in materials and manufacturing processes aim to address these constraints.
Battery Replacement
Battery-powered quartz clocks are popular, but frequent replacements can be inconvenient and costly. Exploring energy-efficient designs and longer-lasting batteries improves the user experience.
Advancements with MEMS Integration
Researchers explore integrating microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) with quartz crystals to enhance precision and stability. This innovation may tackle challenges in traditional quartz-based clock technology.
Acknowledging these challenges propels ongoing research, fostering advancements in quartz-based clock technology. Solutions to these limitations will contribute to improving accuracy, energy efficiency, and design flexibility in quartz clocks as technology continues to evolve.
Conclusion: The Timeless Impact of Quartz on Clock Technology
In conclusion, quartz stands as the cornerstone of clock technology, reshaping the way we measure time with its unique properties and exceptional accuracy. From classic analog to modern digital designs, quartz-based clocks have become synonymous with reliability and affordability.
However, challenges persist, notably in the face of temperature fluctuations, impacting the precision of quartz clocks. While they may not match the craftsmanship of traditional mechanical timepieces, the precision and accessibility of quartz-based clocks continue to outweigh these considerations.
As we look ahead, ongoing research endeavors to further enhance precision and address limitations in quartz-based clock technology, ensuring its continued relevance and evolution. From its initial discovery to its present dominance, quartz remains an indispensable force driving the advancement of timekeeping, with exciting possibilities awaiting the future.